
Inspect the value of variables from a method
Source:R/workflows-inspect.R, R/aliases.R
ggtrace_inspect_vars.RdInspect the value of variables from a method
Usage
ggtrace_inspect_vars(
x,
method,
cond = 1L,
at = "all",
vars,
by_var = TRUE,
...,
error = FALSE
)
inspect_vars(
x,
method,
cond = 1L,
at = "all",
vars,
by_var = TRUE,
...,
error = FALSE
)Arguments
- x
A ggplot object
- method
A function or a ggproto method. The ggproto method may be specified using any of the following forms:
ggproto$methodnamespace::ggproto$methodnamespace:::ggproto$method
- cond
When the return value should be inspected. Defaults to
1L.- at
Which steps in the method body the values of
varsshould be retrieved. Defaults to a special valueallwhich is evaluated to all steps in the method body.- vars
A character vector of variable names
- by_var
Boolean that controls the format of the output:
TRUE(default): returns a list of variables, with their values at each step. This also drops steps within a variable where the variable value has not changed from a previous step specified byat.FALSE: returns a list of steps, where each element holds the value ofvarsat each step ofat. Unchanged variable values are not dropped.
- ...
Unused.
- error
If
TRUE, continues inspecting the method until the ggplot errors. This is useful for debugging but note that it can sometimes return incomplete output.
Tracing context
When quoted expressions are passed to the cond or value argument of
workflow functions they are evaluated in a special environment which
we call the "tracing context".
The tracing context is "data-masked" (see rlang::eval_tidy()), and exposes
an internal variable called ._counter_ which increments every time a
function/method has been called by the ggplot object supplied to the x
argument of workflow functions. For example, cond = quote(._counter_ == 1L)
is evaluated as TRUE when the method is called for the first time. The
cond argument also supports numeric shorthands like cond = 1L which evaluates to
quote(._counter_ == 1L), and this is the default value of cond for
all workflow functions that only return one value (e.g., capture_fn()).
It is recommended to consult the output of inspect_n() and
inspect_which() to construct expressions that condition on ._counter_.
For highjack functions like highjack_return(), the value about to
be returned by the function/method can be accessed with returnValue() in the
value argument. By default, value is set to quote(returnValue()) which
simply evaluates to the return value, but directly computing on returnValue() to
derive a different return value for the function/method is also possible.
Examples
library(ggplot2)
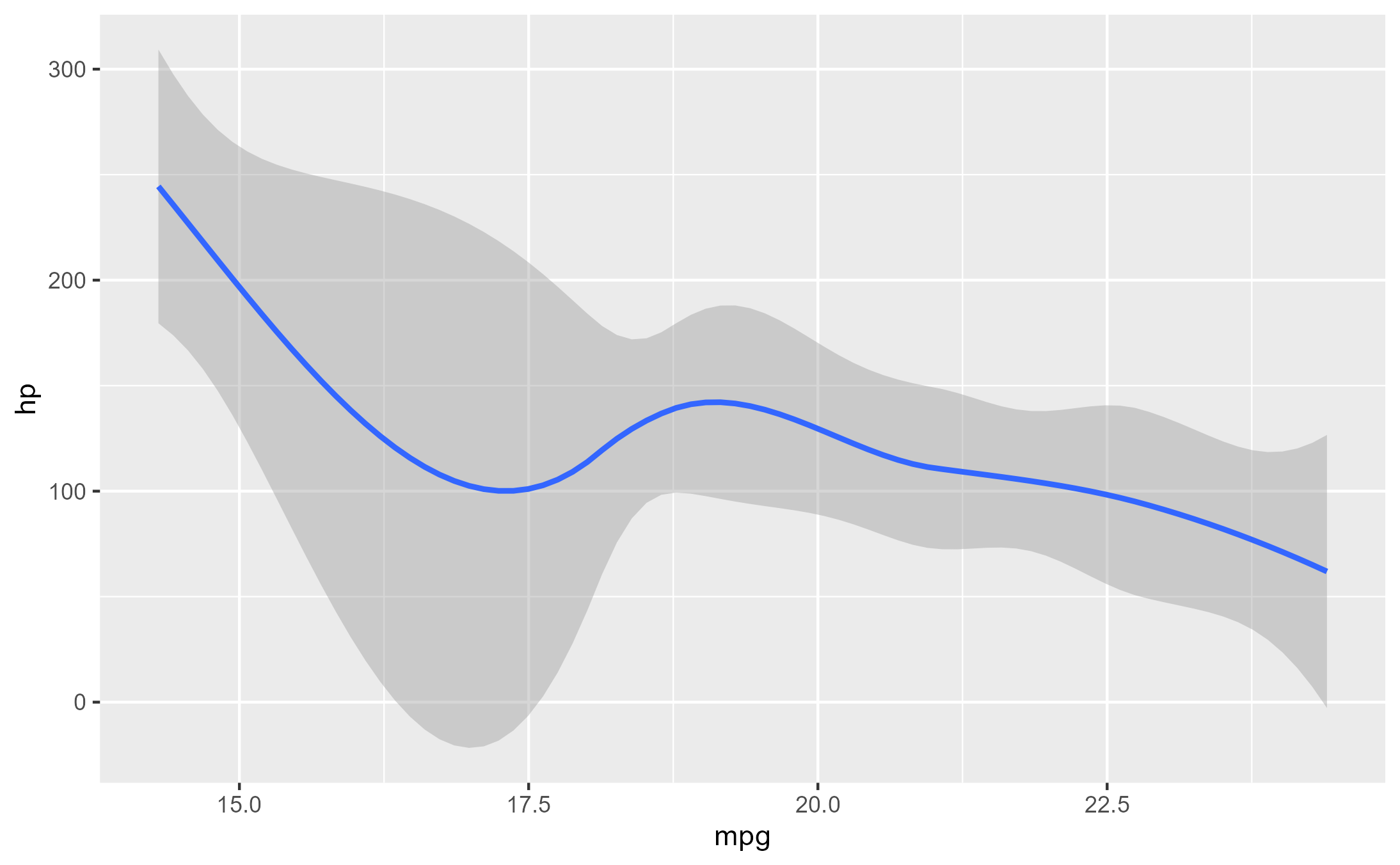
p1 <- ggplot(mtcars[1:10,], aes(mpg, hp)) +
geom_smooth()
p1
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
 # Inspect body of `StatSmooth$compute_group` as list
ggbody(StatSmooth$compute_group)
#> [[1]]
#> `{`
#>
#> [[2]]
#> data <- flip_data(data, flipped_aes)
#>
#> [[3]]
#> if (vec_unique_count(data$x) < 2) {
#> return(data_frame0())
#> }
#>
#> [[4]]
#> if (is.null(data$weight)) data$weight <- 1
#>
#> [[5]]
#> if (is.null(xseq)) {
#> if (is.integer(data$x)) {
#> if (fullrange) {
#> xseq <- scales$x$dimension()
#> }
#> else {
#> xseq <- sort(unique0(data$x))
#> }
#> }
#> else {
#> if (fullrange) {
#> range <- scales$x$dimension()
#> }
#> else {
#> range <- range(data$x, na.rm = TRUE)
#> }
#> xseq <- seq(range[1], range[2], length.out = n)
#> }
#> }
#>
#> [[6]]
#> prediction <- try_fetch({
#> model <- inject(method(formula, data = data, weights = weight,
#> !!!method.args))
#> predictdf(model, xseq, se, level)
#> }, error = function(cnd) {
#> cli::cli_warn("Failed to fit group {data$group[1]}.", parent = cnd)
#> NULL
#> })
#>
#> [[7]]
#> if (is.null(prediction)) {
#> return(NULL)
#> }
#>
#> [[8]]
#> prediction$flipped_aes <- flipped_aes
#>
#> [[9]]
#> flip_data(prediction, flipped_aes)
#>
# The `data` variable is bound to two unique values in `compute_group` method:
inspect_vars(p1, StatSmooth$compute_group, vars = "data")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
#> $Step1
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#> $Step5
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
# With `by_vars = FALSE`, elements of the returned list are steps instead of values
inspect_vars(p1, StatSmooth$compute_group, vars = "data", at = 1:6, by_var = FALSE)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
#> $Step1
#> $Step1$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step2
#> $Step2$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step3
#> $Step3$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step4
#> $Step4$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step5
#> $Step5$data
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
#>
#> $Step6
#> $Step6$data
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
#>
# Inspect body of `StatSmooth$compute_group` as list
ggbody(StatSmooth$compute_group)
#> [[1]]
#> `{`
#>
#> [[2]]
#> data <- flip_data(data, flipped_aes)
#>
#> [[3]]
#> if (vec_unique_count(data$x) < 2) {
#> return(data_frame0())
#> }
#>
#> [[4]]
#> if (is.null(data$weight)) data$weight <- 1
#>
#> [[5]]
#> if (is.null(xseq)) {
#> if (is.integer(data$x)) {
#> if (fullrange) {
#> xseq <- scales$x$dimension()
#> }
#> else {
#> xseq <- sort(unique0(data$x))
#> }
#> }
#> else {
#> if (fullrange) {
#> range <- scales$x$dimension()
#> }
#> else {
#> range <- range(data$x, na.rm = TRUE)
#> }
#> xseq <- seq(range[1], range[2], length.out = n)
#> }
#> }
#>
#> [[6]]
#> prediction <- try_fetch({
#> model <- inject(method(formula, data = data, weights = weight,
#> !!!method.args))
#> predictdf(model, xseq, se, level)
#> }, error = function(cnd) {
#> cli::cli_warn("Failed to fit group {data$group[1]}.", parent = cnd)
#> NULL
#> })
#>
#> [[7]]
#> if (is.null(prediction)) {
#> return(NULL)
#> }
#>
#> [[8]]
#> prediction$flipped_aes <- flipped_aes
#>
#> [[9]]
#> flip_data(prediction, flipped_aes)
#>
# The `data` variable is bound to two unique values in `compute_group` method:
inspect_vars(p1, StatSmooth$compute_group, vars = "data")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
#> $Step1
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#> $Step5
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
# With `by_vars = FALSE`, elements of the returned list are steps instead of values
inspect_vars(p1, StatSmooth$compute_group, vars = "data", at = 1:6, by_var = FALSE)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
#> $Step1
#> $Step1$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step2
#> $Step2$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step3
#> $Step3$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step4
#> $Step4$data
#> x y PANEL group
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1
#>
#>
#> $Step5
#> $Step5$data
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
#>
#> $Step6
#> $Step6$data
#> x y PANEL group weight
#> 1 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 2 21.0 110 1 -1 1
#> 3 22.8 93 1 -1 1
#> 4 21.4 110 1 -1 1
#> 5 18.7 175 1 -1 1
#> 6 18.1 105 1 -1 1
#> 7 14.3 245 1 -1 1
#> 8 24.4 62 1 -1 1
#> 9 22.8 95 1 -1 1
#> 10 19.2 123 1 -1 1
#>
#>